What is Flipped Learning?
The flipped classroom essentially reverses traditional teaching. Instead of teachers talking at students at the front of the room, the learning material is delivered online and consumed by students at home. Whilst classroom time is reserved for ‘homework’, assignments and more hands-on class projects.
The idea is that students absorb the basics of a topic at home, and come to class to strengthen that knowledge by putting it into practice.
Flipped learning not only makes students active participants in the learning process, but also active investigators as they find online resources to share with their peers.
Pros
- Students can pause content, skip ahead, slow down and go at their own pace
- Students can review material multiple times until they understand it
- Students can make study more efficient with learning materials easily accessible & engaging
- Parents can easily review what material their children are learning
- Allows more class time to unpack ideas and physical learning to take place
- Easier for teachers to share materials and techniques
Cons
- Flipped classrooms require teachers to have a higher technical background
- Teachers don’t get immediate feedback & responses from students during content delivery
- Economic hardship on disadvantaged students if they cannot afford their own laptop
- Initial set-up can be lengthy and difficult in the beginning
- Time poor students committed to extracurricular activities may struggle to find time to watch & complete online lectures & activities

What Does Flipped Learning Look Like?
There are 7 different models of flipped classrooms that give us insight into how these classroom operates on a day to day basis.
1. The Standard Inverted Classroom
Students watch videos, podcasts or screen casts made by their teacher as ‘homework’. The next day, students come to class to strengthen that knowledge by putting it into practice through a series of tasks. While the teacher has more time to devote to working with students one-on-one.
2. The Discussion-Oriented Flipped Classroom
The teacher assigns specific lecture videos & readings relating to that day’s topic for students to watch at home and take notes for homework. During class time, the lesson is heavily focused around teacher guided discussion that unpacks and explores the ideas and questions students have.
3. The Demonstration-Focused Flipped Classroom
Teachers create demonstration videos using screen recording software which can be shown during class – especially helpful for chemistry, physics & math. This allows students to rewind, re-watch and work at their own pace without the teacher having to give multiple sets of instructions.
4. The Faux-Flipped Classroom
The videos are played during class time and students take notes. This method often works for younger students who don’t yet have homework assigned to them or their teacher is away.
5. The Group-Based Flipped Classroom
Students watch the videos and take notes for homework as usual. However, during class time, they form learning groups to work together on assessment tasks relevant to the recent video. This format encourages students to not only learn from each other, but also to work together.
6. The Virtual Flipped Classroom
All learning material from instruction, resources, quizzes and assessment is undertaken completely online through LMS. Some colleges, universities and distance education programs operate by sharing lecture videos and readings as well as assigning and collecting work via these online systems.
7. Flipping The Teacher
Students create videos themselves to peer teach and even ‘teach the teacher’. These videos practice role play activities, group presentations or simple demonstrations to help their fellow classmates learn

How Has the Physical Classroom Changed?
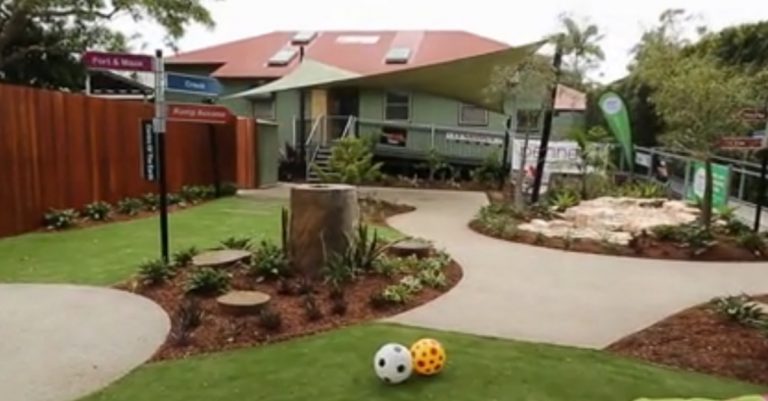
When the teacher and whiteboard are no longer the primary focal point of the classroom, the space can become more flexible and easily adaptable to suite learning activities. With flipped learning, all the instruction and content delivery is consumed at home, leaving more free time in class for hands on activities.
Flipped learning classrooms are collaborative, dynamic and fast paced.
It’s all about providing a mixture of soft seating, agile desking and modular pieces to give students all the fixtures they need to rearrange the space according to how they learn best. Some students will prefer lounging with a laptop and working alone. Some will prefer turning the tables around to form small groups.
Our Top Tips:
- Having interactive surfaces such as whiteboards or glass boards aides in student collaboration, especially brainstorming and unpacking ideas. Kids love having their very own whiteboard surface desk and will actively use it during the day as needed.
- Creating flexible break out spaces promotes active engagement in the classroom. Incorporate lounges, bean bag chairs and reading corners for quiet spaces. Having designated ‘zones’ for group work, individual work, critical reflection and instruction can help diversify the classroom layout.
- The primary classroom should have as much storage as possible, both for students’ personal belongings and for shared writing supplies. Even though the bulk of the learning material may be delivered online, active classrooms still need craft supplies and physical resources like charts, posters and textbooks to visually prompt students during in-class activities.

4 FREE Flipped Classroom Resources
- Ted ED – a fully stocked and extensive online library of educational videos for teachers and students to watch, share and learn from. All for free.
- EDpuzzle – lets teachers find the perfect video, trim the video, add audio clips, and even narrate the whole video. You can add questions during certain parts of the video and create multiple choice questions to check your student’s understanding.
- Google Classroom – lets teachers create online classrooms where students can scroll through a live feed, upload their assignments, access learning materials and interact with their teacher and their peers. Teachers can even grade assignments, upload tasks, schedule announcements as well as create quizzes and polls.
- Screencastify – a handy and easy to use screen casting extension for Google Chrome. It allows teachers to create great content by recording their screen activity to create tutorials.
Still Not Convinced?
–Results from a survey conducted in a flipped Chemistry class revealed that 81% of students found the flipped approach “more useful and/or enlightening”
–At a university of Manchester 74% of 2nd year students & 85% of 4th year students believe “flipped teaching is better than the traditional lecture-based method”
-90% of students consistently watched the screencasts before class.
–Teachers saw a 32% increase in test scores